Related Content
India’s growth story, and the structural transformation it will bring about for our energy and urban systems, will likely be the most significant global shift of the early 21st century, write Rajat Kathuria and Aarsi Sagar.
President Felipe Calderón, Chair of the Global Commission on the Economy and Climate:
The Global Commission on the Economy and Climate and its New Climate Economy project had one of the best months for pressing the momentum for a low-carbon future to media outlets around the world.
Social media analytics show major positive conversation around climate action and economic growth, including most recently at COP21.
"Countries, cities and businesses can achieve not just a better climate, but also better economic growth. We can do well by doing good," writes President Felipe Calderón in USA Today.
"The cost of [fossil fuel] subsidies far outweighs the benefits and burdens the middle classes. Reforming the system can make energy infrastructure more efficient, shore up public finances and allow more targeted spending on public services," writes Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala in Financial Times.
Paris, 5 December, 2015: A new report fr
"Greater ambition on renewable energy and reducing carbon intensity would lead to greater economic benefits for India. It is in our country’s interest to capitalise on the low-carbon economy," writes Naina Lal Kidwai in India Express.
A just transition should encourage all companies to plan ahead for decarbonisation, ensure that workers have the opportunities and skills required to take on new jobs, enable employees to plan for the future, and invest in community renewal, write Sharan Burrow and Paul Polman in Euractiv.
Paris – Former President of Mexico and Chair of the Global Commission on the Economy and Climate, Felipe Calderón, will be in Paris during the UNFCCC Climate Negotiations to lend h
The UN Climate Change Conference (COP21) in Paris is a vital chance to advance a new era of better growth. 24 members of the Global Commission on the Economy and Climate call for stronger climate action ahead of COP 21.
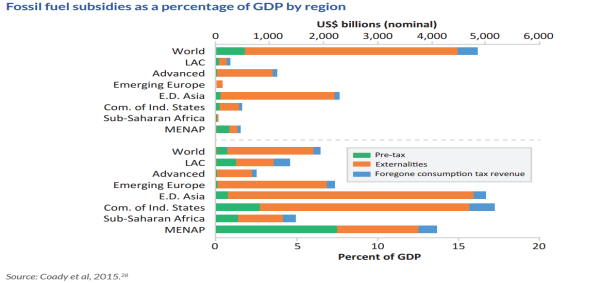
Fossil fuel subsidies take up a huge chunk of countries’ budgets and the world’s GDP.
A new paper by the New Climate Economy identifies the lessons learned from past attempts to reform fossil fuel subsidies, explores why progress has been slow, and outlines the principles for successful reform.
New research from the New Climate Economy shows that raising energy efficiency standards in the G20 and around the world could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 6.9 Gt CO2e per year by 2030, more than the current annual emissions of the United States. These emissions reductions would be accompanied by economic savings in appliances, buildings, industry, and transport.
We must set course to a low-carbon future if we are to avoid the immense risks of climate change, write Ángel Gurría, Sri Mulyani Indrawati and Lord Nicholas Stern in CNN.
A new paper, Implementing effective carbon pricing, from the New Climate Economy shows that carbon pricing works and doesn’t harm the economy. It urges developed and emerging economies, with the G20 in the lead, to commit to introducing carbon prices of roughly comparable levels by 2020.
It is becoming clear that renewables and enhanced energy efficiency, not fossil fuels, will be the solutions to energy poverty, writes Helen Mountford in The Huffington Post.
A new paper from the New Climate Economy shows there is large untapped potential for fuel efficiency gains in both aviation and shipping sectors that would cut costs and reduce emissions. International aviation and shipping have grown dramatically in the last few decades along with their emissions: aviation and shipping now produce 5% of global CO2 emissions, and by 2050, that share could rise to as much as 32%. Much of the potential to reduce emissions in aviation and shipping can be unlocked through existing technologies and practices that leading companies in each sector have already embraced. However, as this new paper shows, market failures and political barriers are hindering progress.
With smarter anti-poverty and energy-access measures and a focus on sustainable finance, the future for Africa and the rest of the developing world can be bright, in more ways than one, writes Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala in The New York Times.